1996/97 Test 3 Parts B & C
To aid you with your exam preparation, the following are the Parts B and C questions from the 1996/97 third midterm. (NOTE: The Part A questions of the 1996/97 third midterm are the questions in Self-Graded Quiz #3.)
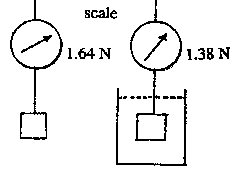
B1. A small object of weight 1.64 N has an apparent weight on the scale of 1.38 N when completely submerged in water. Calculate the volume of the object. Density of water: 1000 kg/m3
B2. A car is moving at 35.0 m/s and approaches a stationary whistle that is emitting a 220-Hz sound. If the speed of sound in air is 343 m/s, what is the frequency heard by the driver?
B3. An organ pipe of length 0.250 m is open at one end and closed at the other. Calculate the second-lowest resonant frequency. The speed of sound in air is 343 m/s.
B4. An electron is placed in a region of space where there is a uniform electric field which is in the +y direction as shown. The magnitude of the electric field is 51.0 V/m. Determine the magnitude and direction of the force on the electron.
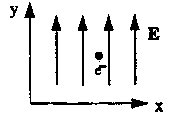
B5. Calculate the diameter of a 2.00-cm length of tungsten filament in a small lightbulb if its resistance is 0.0510 ohms. The resistivity of tungsten is 5.65 × 10-8 ohms·m.
C1. At a distance of 10.0 m from a jackhammer, the sound intensity level is 120 dB. Assume that the sound radiates uniformly in all directions and that no energy is absorbed by the air.
- What is the sound intensity at that distance?
- How far away would you need to be for the sound intensity level to be 85.0 dB?
C3. A point charge, Q = +2.50 × 10-12 C, is fixed in space. Point A is 10.0 cm from Q and point B is 1.00 cm from Q.
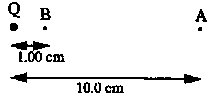
- Calculate the magnitude of the potential difference between points A and B.
- If an electron is released from rest at point A, calculate the speed of the electron when it reaches point B.
Solutions:
- View Page 1 (questions B1, B2)
- View Page 2 (questions B3, B4, B5)
- View Page 3 (question C1)
- View Page 4 (question C2)
- View Page 5 (question C3)

